
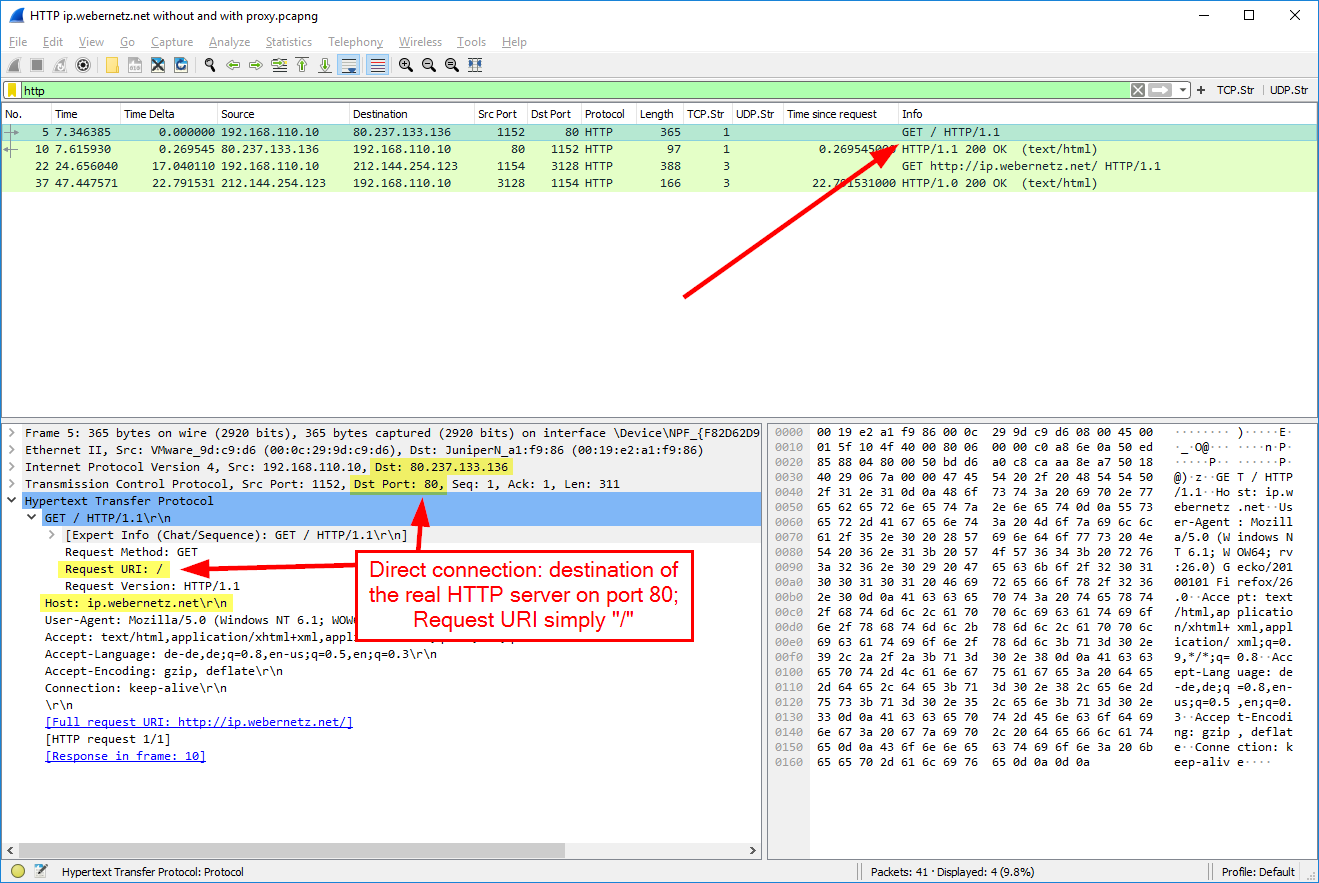
Expand Ethernet and observe the destination address that is the default gateway address whereas, the source is your own MAC address. Input ‘tcp.port = 80’ to see only TCP traffic connected to the webserver connection. Capture the Wireshark traffic while entering the telnet command. Let's analyze a TCP network traffic using telnet on Google port 80. After receiving SYN+ACK, the hacker would send an ACK packet to establish a TCP connection. The port is considered open when he gets SYN+ACK as a response, whereas the arrival of RST shows the port is closed. The attacker sends the SYN packet to the target port. To see more traffic of the target IP (destination IP), input the following filterĪ standard port scan takes advantage of the TCP three-way handshake. Input ' ssl' in the filter box to monitor only HTTPS traffic -> Observe the first TLS packet -> The destination IP would be the target IP (server). Start a Wireshark capture -> Open a web browser -> Navigate to any HTTPS-based website -> Stop the Wireshark capture. The Hypertext Transfer Application Layer Protocol (HTTP) utilizes the internet to establish protocols whenever the HTTP client/server transmits/receives HTTP requests. You can also compare both request and response details, as they are similar. In the response packet, observe the swapping of IPs between source and destination. You can also analyze the ICMP details like Checksum, Identifier Number, Sequence Number, etc. Whereas the destination IP is that of Google. In the request packet, the source IP is your (requestor) IP address. Click the ICMP echo-request packet from the Wireshark capture window and start observing the information. Use the ‘ICMP’ filter to see ICMP traffic.
ICMP is used for error alerting and monitoring to verify whether data arrives in a timely basis at its desired destination. Now, that has turned into your MAC address. The destination and source MAC address are switched in the response packet.Įverything is similar as before, except the target MAC address, which was all zeroes before. Observe the packet replay details from Ethernet and ARP observe the change in source and destination IP and MAC addresses. Since the destination MAC address is unavailable at the request packet stage, the victim's MAC address is zero, and the destination IP is the local system IP address. Observe the packet request details from Ethernet and ARP observe the source and destination IP and sender MAC and IP address. Using the 'arp' filter, analyze the captured traffic in Wireshark. Start Wireshark data capturing, and ping the default gateway address -> Now, let's analyze what happens after removing the ARP entry and pinging a new IP address in the meantime. In our case, it's going to be the default gateway address.įind existing ARP cache -> Delete the existing one to understand the demo -> Check ARP cache for verification. In this demo, let's try capturing and analyzing ARP traffic.įirst things first, know the target machine IP. The most traffic-intensive endpoint, as seen in the picture below, is 192.168.10.4.Īddress resolution protocol (ARP) generally uses to find the MAC address of the target machine. > Click Statistics menu -> Select Endpoints. To analyze the endpoints between two communication devices, do the following:Ĭapture traffic and select the packet whose endpoint you wish to check. This feature comes in handy to determine the endpoint generating the highest volume or abnormal traffic in the network. Some instances are in the following table:įigure 2 Source: Use this technique to analyze traffic efficiently.įollowing the above syntax, it is easy to create a dynamic capture filter, where:įigure 1 Source: But a user can create display filters using protocol header values as well. Wireshark comes with several capture and display filters. Capture filters with protocol header values

This article covers the traffic analysis of the most common network protocols, for example, ICMP, ARP, HTTPS, TCP, etc.
#Wireshark http syntax download#
otherwise, it is available to download from the official website. Wireshark plays a vital role during the traffic analysis it comes pre-installed in many Linux OS’s, for instance, Kali. Network traffic analysis is the routine task of various job roles, such as network administrator, network defenders, incident responders and others. This blog was written by an independent guest blogger.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
